
Chipotle is committed to fresh food in its restaurants
Today, Chipotle is the second highest valued company in the restaurant industry behind McDonald's, with a capitalization of $49.7 billion. But this meteoric rise hasn't been without its bumps.
At the end of 2015, an outbreak of an infectious disease broke out in several restaurants, resulting in hundreds of temporary closures and a significant drop in patronage. The financial impact caused by this scandal was significant. Sales for the year 2016 dropped by more than 20%. This decline was even more painful for the group as profits plunged dramatically from $476 million to $23 million, a drop of 95%. It would take two years (2018) for Chipotle to finally return to its pre-outbreak sales.
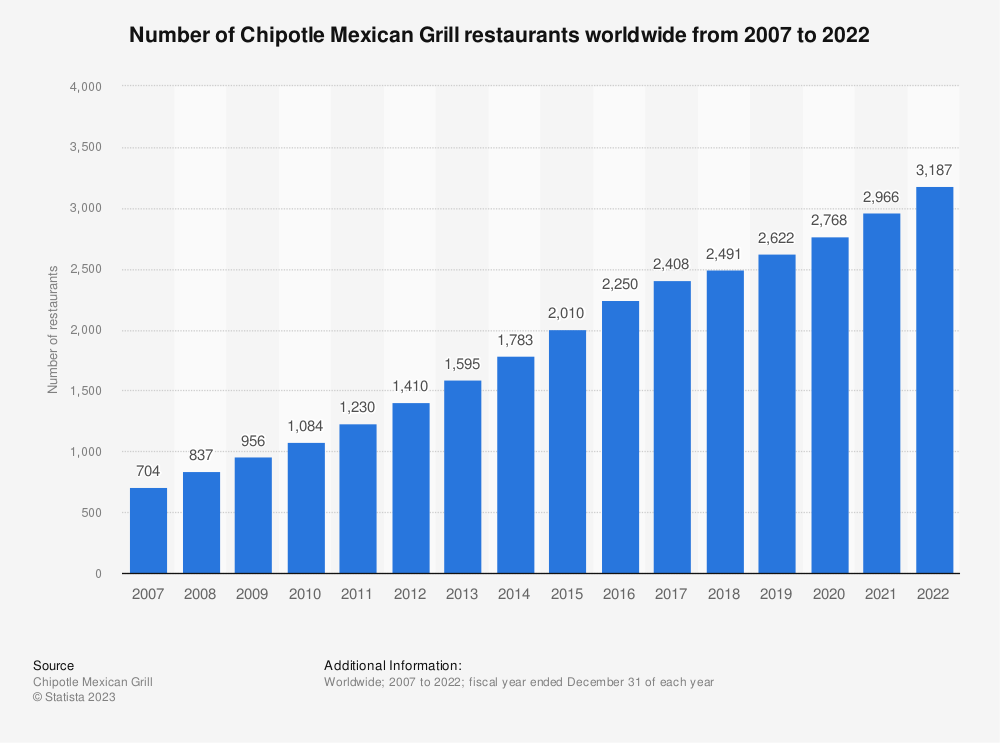
Little by little, the bird is nesting
With annual revenues exceeding $8.6 billion by 2022, exclusively in the United States. The company is considered a "pure player" in food and beverage sales. Although its P/E is high, 42.6 times expected year-end earnings, Chipotle still attracts investors because of its growth potential and a different development strategy than its competitors. Since 2016, Chipotle's revenue and margins have soared. In the span of five years, revenue has doubled while margins have nearly tripled from 3.94% net margin to 10.41% in 2022. COVID has also accelerated online sales, which now account for more than 39.4% of the group's sales in 2022, a sizable share that the group cannot do without.
Chipotle is an exception among its counterparts, such as McDonald's, Taco Bell, Subway, etc. Indeed, the group owns and operates the majority of its restaurants, with only 19 franchised locations, which is an anomaly in an industry that normally grows through the franchise system.
Contrary to what one might think, Chipotle is not in debt to finance its expansion. In fact, the company has always had a positive cash flow, even during difficult times such as the 2016 health scandal and the COVID pandemic. The reasons for this success are many.
First, Chipotle is known for its conservative financial philosophy. The company and executives are focused on maintaining a strong balance sheet and avoiding excessive debt that could hinder its long-term growth and stability.
Chipotle has not engaged in large-scale share buybacks, which could increase its debt levels. Instead, the company has chosen to reinvest its profits in its development to finance its growth and expansion.
Chipotle has pricing power (the ability of a company to increase the price of its products or services without losing market share).
This competitive advantage is based on captive customers who are loyal to the brand because of the superior quality of its products. In this period of inflation, the group has managed to raise its prices steadily (from 8.5% at the end of 2021 to 13% at the end of 2022), but without deterring its customers, who continue to consider the prices reasonable. The reason for this is simple: Chipotle is one of the only fast-food restaurant that offers fresh products, which distinguishes it from its competitors.
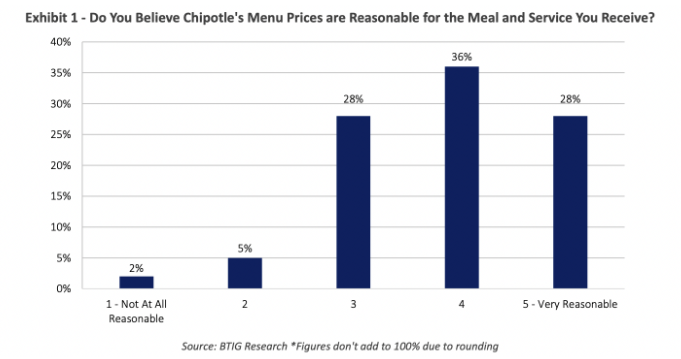
Because of this pricing power, Chipotle has the ability to generate significant cash flow from its operations, giving it the financial flexibility to fund growth without having to take on debt. This ability is a major asset for the company, allowing it to continue to expand while maintaining its long-term financial stability.
As previously mentioned, Chipotle generates significant cash flow. This financial success is due in part to a very efficient supply chain. This means that the group has a low WCR (working capital requirement) and can finance its expansion with its own cash flow. In 2022, the company's Operating Cash Flow (the amount of cash generated by normal business activities), will be 1.32 billion euros.800 million of which has been allocated to investments in properties and equipment. This strategy explains why the group has never opted for the franchise model: it has the means to fully control its fresh produce supply chain, the cornerstone of its success.
A comparison of the working capital of two fast food giants, Chipotle and McDonald's, shows that Chipotle has a much lower working capital of only 11.54 days, compared with 33 days for McDonald's. Working capital refers to the number of days it takes a company to convert working capital into revenue, and in this exercise, Chipotle is three times more efficient than its competitor. In addition, the company's scrupulous management has chosen not to take on any debt, unlike McDonald's, which owes more than $1.3 billion in interest to service its debt by 2022. As a result, Chipotle is able to continue to expand and satisfy its customers while maintaining its financial profitability.
In conclusion, Chipotle is a U.S. fast food company that has experienced tremendous growth despite challenges such as the infectious disease outbreak in 2015. The company's conservative financial strategy and ability to generate strong cash flow have contributed to its success. With the advent of online ordering, it looks poised to maintain its status as a growing pure player in the fast food industry.

 By
By 







